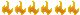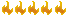The first prototype of the Arjun main battle tank was built in 1984. It was first publicly revealed in 1985. This main battle tank was intended to replace the ageing Vijayanta and Soviet T-72M MBTs in service with the Indian Army. Development process was plagued with delays and to date only 12 prototypes and 32 pre-production vehicles have been built. In 2008 it was announced that there will be no further orders for Arjun tanks. Furthermore India acquired significant number of T-90 MBTs from Russia and plans to manufacture this main battle tank locally. It was reported that a new Arjun Mk.2 MBT is under development. The Arjun MBT has some design similarities with German Leopard 2. It utilizes Kanchan heavy composite armor, which is broadly similar to British Chobham armor. If necessary explosive reactive armor blocks can be added for improved protection. Arjun MBT also incorporates significant crew protection measures, including ammunition compartment separated from the crew with a blow-off panels in the turret bustle.
Vehicle is armed with a 120-mm rifled gun. It is worth mentioning that a rifled gun of such caliber is used only on Challenger 2 MBT. This gun is very accurate at long range and ensures high hit probability. Gun is loaded manually and has a rate of fire of 6 rounds per minute. It is compatible with Israeli LAHAT anti-tank guided missiles, that are launched in the same manner as ordinary munitions. It is claimed that Arjun's fire control system has a hit probability of 90%, when tank is firing on the move.
Secondary armament consists of coaxial 7.62-mm machine gun and roof-mounted 12.7-mm machine gun.
Vehicle has a crew of four, including commander, gunner, loader and driver.
The Arjun MBT is powered by German MTU 838 Ka-501 turbocharged diesel engine, developing 1 400 hp. It uses advanced hydropneumatic suspension. Vehicle is fitted with a self-entrenching blade.





 მთავარი გვერდი
მთავარი გვერდი თამაშები
თამაშები