 |
ტოპ მომხმარებლები |
 |
 |
| Admin Generalissimo | სიახლე: კომენტარი: პოსტი: | 1503 237 217 |
| Checked Major | სიახლე: კომენტარი: პოსტი: | 215 207 29 |
| Moder Major | სიახლე: კომენტარი: პოსტი: | 122 185 87 |
| Admin Colonel general | სიახლე: კომენტარი: პოსტი: | 51 93 11 |
| Checked Private | სიახლე: კომენტარი: პოსტი: | 27 49 5 |
|  |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
Collins class |
 |
 |

Needing a successor to its obsolescent Oberon class diesel-electric submarines, the Royal Australian Navy decided in the first part of the 1980s to consider the full range of foreign-designed submarines that would meet the RAN's operational requirement and also be suitable for construction in an Australian yard. The decision eventually went to a Swedish design, the Type 471 designed by Kockums, and in June 1987 the Australian Submarine Corporation contracted with Kockums for six such submarines, to be built in Adelaide, South Australia, and known in Australian service as the Collins class. The contract included an option for another two boats, but this option was not exercised. Fabrication of the boats initial assemblies began in June 1989, and the bows and midships sections of the first submarines were produced in Sweden and shipped to Adelaide to be mated with locally built sections. The boats were laid down between February 1990 and May 1995, launched between August 1993 and November 2001, and completed between July 1996 and a time in 2003, and are named HMAS Collins, HMAS Farncomb, HMAS Waller, HMAS Dechaineux, HMAS Sheean and HMAS Rankin. The armament and fire control/combat system, the latter proving very troublesome during development and initial service, are along American lines, while the sonar is basically of F
...
კითხვის გაგრძელება »
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
PZL Swidnik W-3 Sokol |
 |
 |

In 1979, with nearly 20 years experience of building Mil-designed helicopters behind it, Poland's PZL Swidnik flew the first prototype of a new design designated W-3 and named Sokol (Flacon). There was a long series of tethered tests and extensive design changes before the second prototype flew in May 1982, and it was another three years before production began. Since then, PZL has developed several specialized variants for military and civil applications. By 1996 PZL had completed more than 80 production W-3s, including 12 for Myanmar. Others were built for the Polish armed forces and government agencies, and included naval, fire-fighting and search and rescue (SAR) models. Known as the Anakonda, the W-3RM is a rescue variant with flotation bags, a watertight cabin and a winch. The W-3U-1 Alligator was proposed for the anti-submarine role, but the planned W-3 Sokol-Long, with a stretch fuselage seating up to 14 fully armed troops, was discontinued in 1993. W-3s have been fitted with several different weapons, including AT-6 Spiral anti-tank and SA-7 Grail anti-aircraft missiles, 20-mm and 23-mm cannon, and rocket launchers. At one stage, the manufacturer teamed with Kentron of South Africa to offer an export version with weapons systems similar to those of the Denel AH-2 Rooivalk, but the partnership failed in 1994. In its ba
...
კითხვის გაგრძელება »
|
 |
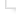 |
 |
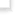 |
 |
Boeing Helicopters CH-47 Chinook |
 |
 |

Though the US Army was initially interested in the Vertol 107 (which became the H-46 Sea Knight), in 1959 it finally picked a much bigger project, under development since 1956. The prototype Boeing Vertol Model 114 Chinook flew on 21 September 1961, and since then over 1 160 have been built, including 136 from Agusta (Meridionali) in Italy and 54 by Kawasaki in Japan (CH-47J). The original CH-47A reached the US Army in December 1962, and Vertol built 349 before delivering 108 CH-47Bs with more powerful engines, followed by 233 CH-47Cs with 3 750-shp (2798-ekW) engines, increased fuel and, as a retrofit, glass fibre blades and blade-inspection systems. Boeing and Meridionali have sold Chinooks all over the world, export models including the Canadian CH-147 and RAF Chinook HC.Mk 1. The HC.Mk 1 was delivered with two cargo hooks, one rated at 9 000 kg and the other at 11 300 kg, and comprehensive nav/com avionics. Between 1982 and 1998 over 480 of the US Army's Chinooks were remanufactured to CH-47D standard with greatly enhanced capability; the RAF has also upgraded 32 of its surviving Chinooks to this standard as Chinook HC.Mk 2s and also received a further eight new-build HC.Mk 2s, as well as nine HC.Mk 3s, which are similar to the US Army's MH-47E special missions helicopter. Other nations operatin
...
კითხვის გაგრძელება »
|
 |
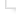 |
 |
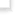 |
 |
Tupolev Tu-22M Backfire |
 |
 |

The Tu-22M was developed from the earlier Tu-22 design, incorporating variable-geometry outer wing panels. The first Tu-22M-0 prototype flew in 1969. Powered by a military derivative of the engine originally designed for the Tu-144 supersonic airliner, the Backfire is extremely fast, even at low level. The Tu-22M lacks sufficient range for truly strategic missions and is classified as a medium bomber. The first series production model was the Tu-22M-2 Backfire-B (211 built) for the Soviet Air Forces and the Naval Aviation Forces. Normally armed with a single Kh-22 stand-off missile, this variant became operational with 185 Guard Heavy Bomber Aviation Regiment at Poltava in 1978, and also served in Afghanistan. The ultimate bomber/missile carrying variant is the Tu-22M-3 Backfire-C, (268 built). The M-3 features strengthened wings, raked rectangular intakes serving more powerful engines. It also had a greatly increased weapons load (see specification). The Tu-22M3 remains numerically the most important bomber in the Russian air force's Long-Range Air Army inventory, and serves with seven regiments (one of which also operates Tu-22M-2s). The Naval Aviation Forces have about 80 Tu-22Ms, mostly M-3 models, split equally between divisions subordinated to the Northern and Pacific Fleets. The Naval Aviation Forces also have 12 M-3s conver
...
კითხვის გაგრძელება »
|
 |
 |
 |
 | « 1 2 ... 8 9 10 11 12 ... 32 33 » |
|
 |
მეგობრები |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 | |



